Answer:
Greater than
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, angular momentum is conserved.
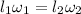
When the cloud shrinks under the right conditions, a star may be formed.
Thus, Diameter of clouds are much higher than a star.
Moment of inertia of cloud is greater than the star's inertial.
so, angular velocity of the star would be greater than angular velocity of the rotating gas.