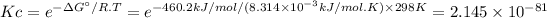Answer:
Kc = 2.145 × 10⁻⁸¹
Step-by-step explanation:
Let's consider the following reaction:
O₂(g) ⇄ 2O(g)
The standard Gibbs free energy for the reaction (ΔG°) can be calculated using the following expression:
ΔG° = Σnp. ΔG°f(p) - Σnp. ΔG°f(p)
where,
ni are the moles of products and reactants
ΔG°f(p) are the standard Gibbs free energy of formation of products and reactants
In this case,
ΔG° = 2 × ΔG°f(O) - 1 × ΔG°f(O₂)
ΔG° = 2 × 230.1 kJ/mol - 1 × 0 kJ/mol
ΔG° = 460.2 kJ/mol
With this information, we can calculate the equilibrium constant (Kc) using the following expression: