Answer:
The standard reaction enthalpy for the given reaction is 235.15 kJ/mol.
Step-by-step explanation:
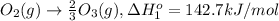 ..[1]
..[1]
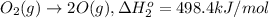 ..[2]
..[2]
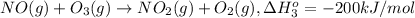 ..[3]
..[3]
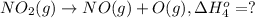 ..[4]
..[4]
Using Hess's law:
Hess’s law of constant heat summation states that the amount of heat absorbed or evolved in a given chemical equation remains the same whether the process occurs in one step or several steps.
2 × [4] = [2]- (3 ) × [1] - (2) × [3]
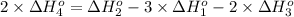
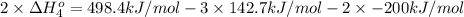
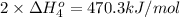
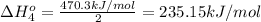
The standard reaction enthalpy for the given reaction is 235.15 kJ/mol.