Answer:
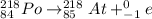 is the correct equation for beta decay.
is the correct equation for beta decay.
Step-by-step explanation:
When a beta particle, that is,
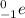 is emitted in a radioactive decay then it is known as beta decay.
is emitted in a radioactive decay then it is known as beta decay.
Therefore, beta decay of Polonium-218 is as follows.
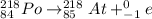
Therefore, we can conclude that
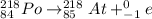 is the correct equation for the given beta decay.
is the correct equation for the given beta decay.