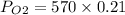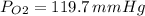Answer:
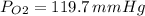
Step-by-step explanation:
The composition of atmospheric air is approximately 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen, 1% argon, and trace percentages of carbon dioxide, neon, methane, helium, krypton, hydrogen, xenon, ozone, nitrogen dioxide, iodine, carbon monoxide, and ammonia.
At sea level where the atmospheric pressure is known to be 760 mm Hg, the partial pressures of the various gases can be estimated to have partial pressures of approximately 593 mm Hg for nitrogen, 160 mm Hg for oxygen, and 7.6 mm Hg for argon.
However, these partial pressures are not accurate reflections of the partial pressures available because of the presence of water vapour and other suspended particulate matter.
Given:
Total pressure at the top of mountain,
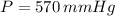
∵Oxygen contributes 21% of the atmospheric gases, we use this as the factor in the atmospheric pressure.