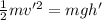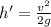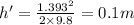Answer:
Final speed is 8.506 m/s
Height of the block is 0.1 m
Solution:
As per the question:
Mass of the smaller block, m = 5 kg
Height of the track, h = 5 m
Mass of the larger block, M = 18 kg
Now,
To calculate the final speed of the larger block:
Consider that both the momentum and the energy of the block is conserved as the track is friction-less.
If the smaller block is at a height 'h' then it will have potential energy only.
The initial energy of the entire system is ;
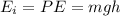
As it starts moving on the track, the potential energy is completely transfomed into Kinetic energy that provides motion, thus the final enrgy:
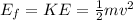
Following the conservation of energy:
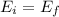
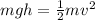
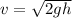
Since, the collision is elastic, both Kinetic energy of the blocks and the momentum are conserved.
Now,
Initial Momentum,
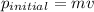
Final Momentum,
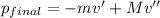
Now, by the conservation of momentum:
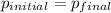
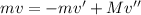
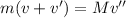 (1)
(1)
From the conservation of kinetic energy:
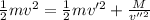
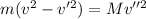 (2)
(2)
Dividing eqn (1) and (2), we get:
v = v' + v''
Also, from above, we can write:
v' + v'' =
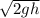
v' + v'' =
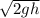
v' =
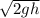 - v'' (3)
- v'' (3)
Using eqn (3) in eqn (1) and (2) and solving we get:
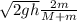
Using proper values in the above eqn:
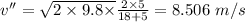
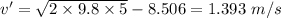
Now, the Kinetic energy required to climb the curve:
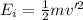
Now, at height h':
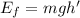
By the conservation of energy principle: