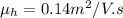Answer:
0.5m^2/Vs and 0.14m^2/Vs
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the mobility of electron and mobility of hole for gallium antimonide we have,
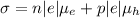 (S)
(S)
Where
e= charge of electron
n= number of electrons
p= number of holes
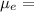 mobility of electron
mobility of electron
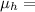 mobility of holes
mobility of holes
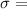 electrical conductivity
electrical conductivity
Making the substitution in (S)
Mobility of electron
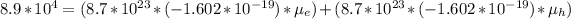
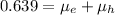
Mobility of hole in (S)
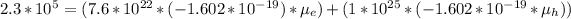

Then, solving the equation:
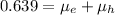 (1)
(1)
 (2)
(2)
We have,
Mobility of electron
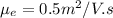
Mobility of hole is