Answer:
1.8 mm
Step-by-step explanation:
given data
thick = 2.5 mm
flux = 1 ×
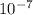 kg/m²
kg/m²
high pressure surface is 2 kg/m³
solution
we use fick first law for steady state diffusion
J = D ×
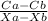 ..........1
..........1
we take here Ca to point which concentration of nitrogen is 2 kg/m³
so we solve Xb
Xb = Xa + D ×
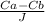
assume Xa = 0 at surface
Xb = 0 + ( 12 ×
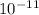 ) ×
) ×
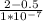
Xb = 1.8 ×
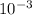
Xb = 1.8 mm