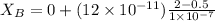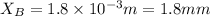Answer:
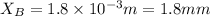
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data:
Diffusion constant for nitrogen is
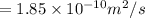
Diffusion flux
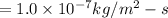
concentration of nitrogen at high presuure = 2 kg/m^3
location on which nitrogen concentration is 0.5 kg/m^3 ......?
from fick's first law
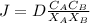
Take C_A as point on which nitrogen concentration is 2 kg/m^3
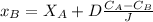
Assume X_A is zero at the surface