Answer:
(a) Limiting reactant = HCl
(b) 0.33 moles Cl₂
(c) 0.26 moles Cl₂
Step-by-step explanation:
The equation is:
4HCl(aq) + MnO₂(s) → MnCl₂(aq) + 2H₂O(l) + Cl₂(g) (1)
We have:
m MnO₂ = 42.5 g
m HCl = 47.7 g
M HCl: molar mass = 36.46 g/mol
M MnO₂ = 86.94 g/mol
The number of moles (η) of HCl and MnO₂ is:
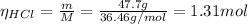
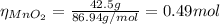
(a) From equation (1) we have that 4 moles of HCl reacts with 1 mol of MnO₂, so the limiting reactant is:
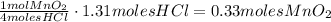
We can see that we need 0.33 moles of MnO₂ to react with HCl, but we have 0.49 moles in total, hence, the MnO₂ is in excess and the limiting reactant is HCl.
(b) The theoretical yield of Cl₂ (not CO₂) is the following:
From equation (1) we have that 4 moles of HCl produces 1 mol of Cl₂, hence the moles of Cl₂ produced is:
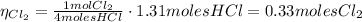
Hence, the theoretical yield of Cl₂ is 0.33 moles.
(c) The actual yield of Cl₂ is:
% = (actual yield*100)/(theoretical yield)
actual yield = 0.799*0.33 moles = 0.26 moles Cl₂.
Therefore, the actual yield of Cl₂ is 0.26 moles.
I hope it helps you!