Answer:
-2200 N
Step-by-step explanation:
Here we can use the impulse theorem, which states that the impulse exerted on Sarah (product of force and duration of collision) is equal to Sarah's change in momentum:
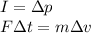
where
F is the average force
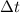 is the duration of the collision
is the duration of the collision
m is the mass
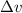 is the change in velocity
is the change in velocity
In this problem:
m = 55 kg
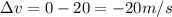
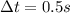
Solving the formula, we find the force exerted by the seatbelt on Sarah:
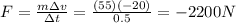
And the negative sign means the direction is opposite to that of Sarah's initial motion.