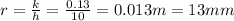Answer:
maximum allowable electrical power=4.51W/m
critical radius of the insulation=13mm
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello!
To solve this heat transfer problem we must initially draw the wire and interpret the whole problem (see attached image)
Subsequently, consider the heat transfer equation from the internal part of the tube to the external air, taking into account the resistance by convection, and conduction as shown in the attached image
to find the critical insulation radius we must divide the conductivity of the material by the external convective coefficient