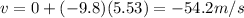1) 237.8 m
We start by considering the vertical motion of the package. This is a free fall motion (uniform accelerated motion). For this, we can use the suvat equation:
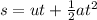
where
, chosing downward as positive direction,
s = 150 m is the vertical displacement
u = 0 is the initial vertical velocity of the package
t is the time
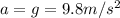 is the acceleration of gravity
is the acceleration of gravity
Solving for t, we find the time at which the package reaches the ground (time of flight):
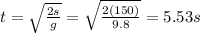
Let's now consider the horizontal motion of the package: this is a uniform motion, since the package mantains its initial horizontal velocity (the same as the plane). The horizontal distance travelled is given by the package is
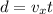
where
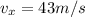 is the horizontal velocity of the package
is the horizontal velocity of the package
t = 5.53 s is the time of flight
Solving for d,
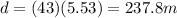
Therefore, the package lands 237.8 m away from the point directly below where it was released.
2) 43 m/s
The motion of the package along the horizontal direction is a uniform motion: it means that the horizontal component of the velocity is constant. Since its initial horizontal velocity was equal to the velocity of the plane, 43 m/s, it means that the final component of the horizontal velocity is exactly the same, 43 m/s.
3) -54.2 m/s
The vertical component of the velocity of the package just before hitting the ground can be calculated using the suvat equation
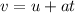
where
u = 0
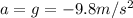 is the acceleration of gravity (here we have chosen upward as positive direction, so the acceleration is negative, since it is downward)
is the acceleration of gravity (here we have chosen upward as positive direction, so the acceleration is negative, since it is downward)
t = 5.53 s is the time of flight
Substituting,