Answer:
q=1910.71 W/m²
T=383.07 K
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that
L₁=0.25 m ,K₁=1.13 W/(m.K)
L₂=0.2 m , K₂=1.45 W/(m.K)
L₃= 0.1 m , K₃=0.66 W/(m.K)
h₁=115 W/(m².K)
h₂=23 W/(m².K)
The total thermal resistance
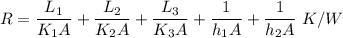
Now by putting the values
Put A= 1 m² ( To find heat transfer per unit area)
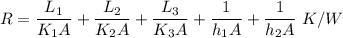
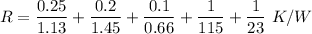
R= 0.56 K/W
We know that
q= ΔT/R
Here ΔT = 1370 - 300 K =1070 K
Now by putting the values
q= 1070/0.56
q=1910.71 W/m²
Lets T is the outside surface temperature
q = h₂ ( T- 300)
Now by putting the values
1910.71 = 23 ( T- 300)
T=383.07 K