Answer:
Vn/Ve = B
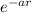
Step-by-step explanation:
To establish this relationship we must examine the potentials that these forces create. The electrical potential is described by
Ve = k q / r
The potential for strong nuclear force is
Vn (r) = - gs / 4pir exp (-mrc / h)
Where gs is the stacking constant and r the distance between the nucleons,
We can compare these potentials where the force is derived from the relationship
E = -dU / dr
F = q E
The case of the electric potential varies with the inverse of the distance, in the distance between two nucleons is very strong
The case of strong nuclear potential has a competition between two factors:
- The inverse of the distance that is equal to the electromagnetic
- The negative exponential whose variation for small values of r is much greater than the inverse term of the distance and dominates the potential
Let's make an approximate relationship
Vn / Ve = [- gs / 4pir exp (-mrc / h)] / [k q / r]
Let's separate the constants and simplify the variables
Vn / Ve = [-gs / (4pi k q1)] exp (-A r)
A = mc / h
Vn/Ve = B
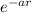
Vn = B Ve / exp (A r)
When r decreases the nuclear potential is the one that dominates.