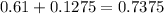Answer:
P(μ-σ ≤ X ≤ μ+σ) =
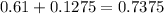
Explanation:
The geometric distribution is the number of failures expected before you get a success in a series of Bernoulli trials.
It has the following probability density formula:
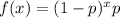
In which p is the probability of a success.
The mean of the geometric distribution is given by the following formula:
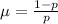
The standard deviation of the geometric distribution is given by the following formula:
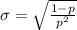
In this problem, we have that:
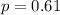 .
.
So
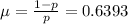
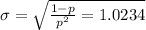
P(μ-σ ≤ X ≤ μ+σ) =
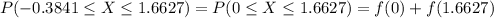
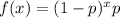
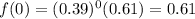
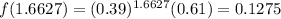
P(μ-σ ≤ X ≤ μ+σ) =