Answer:
Momentum is conserved when the net external force on the system is zero
Step-by-step explanation:
Here we call 'system' the two objects together.
It is possible to demonstrate that the total momentum of a system is conserved when the net external force acting on it is zero. In fact, Newton's second law states that:
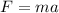
where F is the net external force, m the mass of the system, a its acceleration.
Re-writing the acceleration as rate of change of velocity:
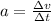
we get:
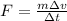
However, assuming that the mass of the system does not change, the quantity at the numerator is just the change in momentum of the system:
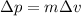
So the equation becomes:
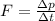
And therefore, if the net external force on the system is zero, F = 0, we get
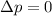
which means that the total momentum is conserved.