Answer:
They differ in a 5.86%
Step-by-step explanation:
Hi, the Van der Waals equation for gases is:

For methane gas:
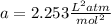
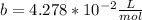
The conditions give{n are T=271.3 K, n=1.052mol and V=1.031L
The molar volume:
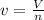
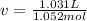
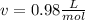
Replacing in Van der Waals :
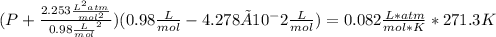
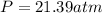
In percentaje:
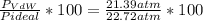
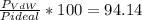
They differ in a 5.86%