Answer:
a) ΔHvap=35.3395 kJ/mol
b) Tb=98.62 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the reaction:
C₇H₁₆ (l) ⇔ C₇H₁₆ (g)
Kp=P(C₇H₁₆) since the concentration ratio for a pure liquid is equal to 1.
When
T₁=50°C=323.15K ⇒P₁=0.179
T₂=86°C=359.15K ⇒P₂=0.669
The Clasius-Clapeyron equation is:
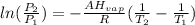
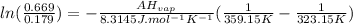
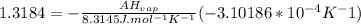
ΔHvap=35339.5 J/mol=35.3395 KJ/mol
Normal boiling point ⇒ P=1 atm
Hence, we find the normal boiling point where:
T₁=323.15K
P₁=0.179 atm
P₂=1 atm
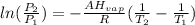
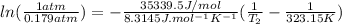
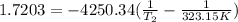
T₂=371.77 K= 98.62 °C