Answer:
There are 1.83 moles present in 130 g of chlorine gas.
Step-by-step explanation:
The rule of three or is a way of solving problems of proportionality between three known values and an unknown value, establishing a relationship of proportionality between all of them. That is, what is intended with it is to find the fourth term of a proportion knowing the other three. Remember that proportionality is a constant relationship or ratio between different magnitudes.
If the relationship between the magnitudes is direct, that is, when one magnitude increases, so does the other (or when one magnitude decreases, so does the other) , the direct rule of three must be applied. To solve a direct rule of three, the following formula must be followed:
a ⇒ b
c ⇒ x
Then:
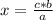
In this case, the rule of three can be applied as follows: if the molar mass indicates that 70.9 g of gaseous chlorine are present in 1 mol of the gas, 130 g will be present in how many moles of the gas?
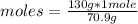
moles=1.83
There are 1.83 moles present in 130 g of chlorine gas.