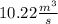Answer:
10.22 m^3/s
Step-by-step explanation:
To estimate the pressure drop in a pipe we use the Darcy-Weisbach equation
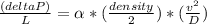 (equation 1)
(equation 1)
With:
 = Darcy-Weisbach friction coefficient
= Darcy-Weisbach friction coefficient
L = length of duct or pipe
v = velocity of fluid
D= hydraulic diameter
Also flow rate is:
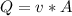
Where v is:
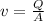
Area as a function of the diameter is:
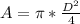
So
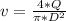 (equation 2)
(equation 2)
For a laminar regime the the Darcy-Weisbach friction coefficient is function of the Reynolds number (Re) as:
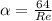
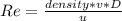
With: v =velocity, D= diameter if the pipe and u= viscosity.
With this information alpha would be:
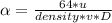 (equation 3)
(equation 3)
Replacing equation 3 in equation 1 we have:
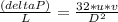
And finally replacing the value for v in this equation we have:
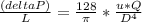
Clearing for Q we get an expression to estimate the expected flow rate in the pipe.
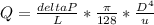
We know
Delta P = 1.84 psi or
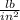
L= 75 ft or 900 in
D for a 2 nominal schedule 40 PVC is 2.047 in. In tables you find External diameter and internal diameter. For calculations you use internal diameter (ID)
U for water at 20°C is
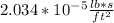 or
or
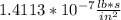
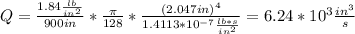
So the flow expected for this pipe is
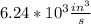 or
or