Answer:
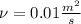
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
Kinematic viscosity is defined in terms of the dynamic viscosity as follows:
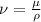
Whereas
 is the kinematic viscosity,
is the kinematic viscosity,
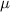 the dynamic viscosity and
the dynamic viscosity and
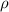 the density. In this case, the given temperature and pressure are defining both
the density. In this case, the given temperature and pressure are defining both
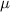 and
and
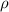 so they are not included into the aforesaid equation, in such a way, the kinematic viscosity is straightforwardly computed as shown below:
so they are not included into the aforesaid equation, in such a way, the kinematic viscosity is straightforwardly computed as shown below:
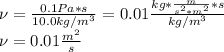
Best regards.