Step-by-step explanation:
It is given that,
Initial speed of the car, u = 57.7 km/hr = 16.02 m/s
Distance between the car and the barrier, d = 22.2 m
The car hits the barrier 2.14 s later.
Final speed of the car, v = 0 (at rest)
Let a is the acceleration of the car. It can be calculated using the second equation of motion as :
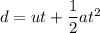
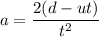
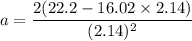
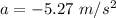
As the car decelerates, the acceleration of the car just before the impact is
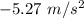 . Hence, this is the required solution.
. Hence, this is the required solution.