Answer:
a.) a = 0 ms⁻²
b.) a = 9.58 ms⁻²
c.) a = 7.67 ms⁻²
Step-by-step explanation:
a.)
Acceleration (a) is defined as the time rate of change of velocity
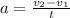
Given data
Final velocity = v₂ = 0 m/s
Initial velocity = v ₁ = 0 m/s
As the space shuttle remain at rest for the first 2 minutes i.e there is no change in velocity so,
a = 0 ms⁻²
b.)
Given data
As the space shuttle start from rest, So initial velocity is zero
Initial velocity = v₁ = 0 ms⁻¹
Final velocity = v₂ = 4600 ms⁻¹
Time = t = 8 min = 480 s
By the definition of Acceleration (a)
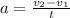
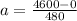
a = 9.58 ms⁻²
c.)
Given data
As the space shuttle is at rest for first 2 min then start moving, So initial velocity is zero
Initial velocity = v₁ = 0 ms⁻¹
Final velocity = v₂ = 4600 ms⁻¹
Time = t = 10 min = 600 s
By the definition of Acceleration (a)
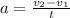
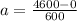
a = 7.67 ms⁻²