Answer : The mass of oxygen present in the flask is 0.03597 grams.
Explanation :
First we have to determine the moles of
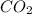 gas.
gas.
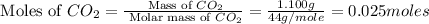
Now we have to calculate the moles of the oxygen gas.
Using ideal gas equation:
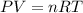
As, the moles is an additive property. So,
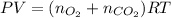
where,
P = pressure of gas = 608 mmHg = 0.8 atm
(conversion used : 1 atm = 760 mmHg)
V = volume of gas = 1 L
T = temperature of gas = 373 K
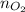 = number of moles of oxygen gas = ?
= number of moles of oxygen gas = ?
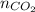 = number of moles of carbon dioxide gas = 0.025 mole
= number of moles of carbon dioxide gas = 0.025 mole
R = gas constant =
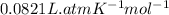
Now put all the given values in the ideal gas equation, we get:
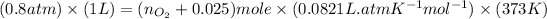
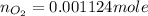
Now we have to calculate the mass of oxygen gas.
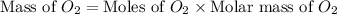
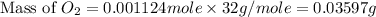
Therefore, the mass of oxygen present in the flask is 0.03597 grams.