Answer:
Given that a person was identified as a future terrorist, there is a 2.8544% probability that he/she actually is a future terrorist.
Explanation:
There are 1000 future terrorists in a population of 300,000,000. So the probability that a randomly selected person in this population is a terrorist is:
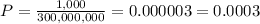
So, we have these following probabilities:
A 99.9997% probability that a randomly chosen person is not a terrorist.
A 0.0003% probability that a randomly chosen person is a terrorist.
A 98% probability that a future terrorist is correctly identified
A 99.9% chance of correctly identifying someone who is not a future terrorist. This also means that there is a 0.01% probability of someone who is not a terrorist being identified as one.
This can be formulated as the following problem:
What is the probability of B happening, knowing that A has happened.
It can be calculated by the following formula
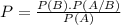
Where P(B) is the probability of B happening, P(A/B) is the probability of A happening knowing that B happened and P(A) is the probability of A happening.
Here we have:
What is the probability that the person is a terrorist, given that she was identified as a terrorist.
P(B) is the probability that the person is a terrorist. So
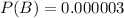
P(A/B) is the probability that the person was identified as a terrorist, given that she is a terrorist. The problem states that the system has a 98% chance of correctly identifying a future terrorist, so
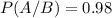
P(A) is the probability of a person being a identified as a terrorist. So
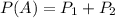
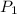 is the probability that a person is a terrorist and was identified as one. So:
is the probability that a person is a terrorist and was identified as one. So:
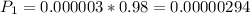
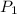 is the probability that a person is not a terrorist and, but was identified as one. So:
is the probability that a person is not a terrorist and, but was identified as one. So:
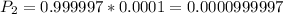
So
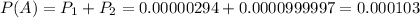
The answer is:
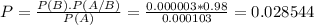
Given that a person was identified as a future terrorist, there is a 2.8544% probability that he/she actually is a future terrorist.