Step-by-step explanation:
(a) When oxidation of glucose occurs the glucose molecules react with oxygen and it results in the formation of carbon dioxide and water.
And, when in a chemical reaction equation number of atoms on the reactant side are equal to the number of atoms on product side then it is known as a balanced equation.
For example,
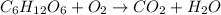
Number of atoms on reactant side are as follows.
C = 6
H = 12
O = 8
Number of atoms on product side are as follows.
C = 1
H = 2
O = 3
Therefore, balance this equation by multiplying
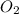 by 6 on reactant side. Also, on reactant side multiply
by 6 on reactant side. Also, on reactant side multiply
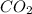 by 6 and
by 6 and
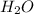 by 6.
by 6.
Hence, the balanced equation is as follows.
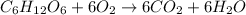
(b) According to the reaction equation, to completely oxidize 1 mole of glucose we need 6 mole of
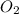 .
.
Therefore, to completely oxidize 180 g of glucose we need,
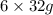 of
of
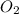 .
.
So, calculate the the amount of
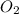 required to completely oxidize 1 g of glucose as follows.
required to completely oxidize 1 g of glucose as follows.
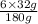 g of
g of
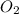
= 1.07 g
Thus, we can conclude that the mass of
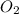 required to completely oxidize 1 g of glucose is 1.07 g.
required to completely oxidize 1 g of glucose is 1.07 g.