Step-by-step explanation:
In a chemical reaction equation, if number of atoms on the reactant side are equal to the number of atoms on product side then it is known as a balanced equation.
And, a redox reaction is defined as the reaction where there occurs change in the oxidation states of the reactants.
For example,
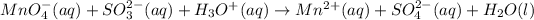
Reduction-half reaction:
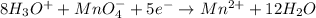 ....... (1)
....... (1)
Oxidation-half reaction:
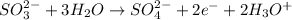 ............. (2)
............. (2)
Now, we multiply equation (1) by 2 and multiply equation (2) by 5.
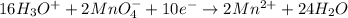 ......... (3)
......... (3)
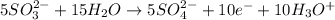 ......... (4)
......... (4)
Now, add both of equations (3) and (4) and the balance equation will be as follows.
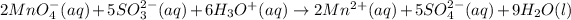
Hence, the coefficient of
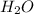 is 9.
is 9.