Answer: Option (4) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
Relation between potential energy and charge is as follows.
U =
![(1)/(4 \pi \epsilon_(o))[(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12)) + (q_(2)q_(3))/(r_(23)) + (q_(3)q_(1))/(r_(31))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/xdyzkp7c61y8b5va8o6x10tevxk3ur1f5e.png)
As it is given that
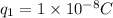 ,
,
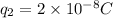 , and
, and
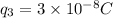 .
.
Distance between the charges = 1 cm =
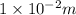 (as 1 cm = 0.01 m)
(as 1 cm = 0.01 m)
Hence, putting these given values into the above formula as follows.
U =
![(1)/(4 \pi \epsilon_(o))[(q_(1)q_(2))/(r_(12)) + (q_(2)q_(3))/(r_(23)) + (q_(3)q_(1))/(r_(31))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/xdyzkp7c61y8b5va8o6x10tevxk3ur1f5e.png)
=
![9 * 10^(9) [(1 * 10^(-8) * 2 * 10^(-8))/(10^(-2)) + (2 * 10^(-8) * 3 * 10^(-8))/(10^(-2)) + (3 * 10^(-8) * 1 * 10^(-8))/(10^(-2))]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/royv80emted9ciz0bwse2h8493uhde3hl6.png)
=
![9 * 10^(9) [2 + 6 + 1.5]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/3qa32cer1dm16qbx6ggiah79vvus3yfwx8.png)
=
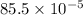 J
J
= 0.00085 J
Thus, we can conclude that the potential energy of this arrangement, relative to the potential energy for infinite separation, is about 0.00085 J.