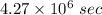Answer:
(a). The drift velocity is
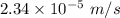 .
.
(b). The time is
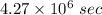
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that,
Radius = 1 mm
Current = 1 A
Distance = 100 m
(a). We need to calculate the drift speed
Using formula of drift velocity
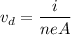
Where, i = Current
n = number density
e = charge on electron
A = area cross section
We know that,
The molar mass of copper is 63.55 g/mol.
The mass density is 8.96 g/cm³.
We need to calculate the number of density
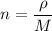
Put the value into the formula
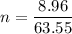
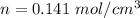
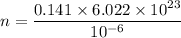
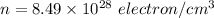
Put the value into the formula of drift velocity
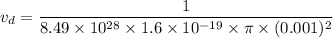
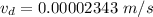
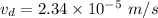
(b). We need to calculate the time
Using formula of distance
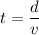
Put the value into the formula
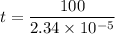
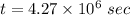
Hence, (a). The drift velocity is
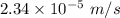 .
.
(b). The time is