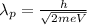Answer:
Wavelength of the particle is
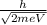
Solution:
As per the question:
The particle with mass, m and charge, e accelerates through V (potential difference).
The momentum of the particle,
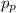 if it travels with velocity,
if it travels with velocity,
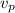 :
:
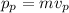
Now, squaring both sides and dividing by 2.
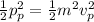
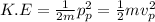
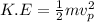
Also,
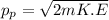 (1)
(1)
Now, we know that Kinetic energy of particle accelerated through V:
K.E = eV (2)
where
e = electronic charge =
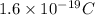
From eqn (1) and (2):
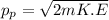 (3)
(3)
From eqn (2) and (3):
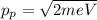
From the de-Broglie relation:
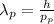 (4)
(4)
where
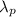 = wavelength of particle
= wavelength of particle
h = Planck's constant
From eqn (3) and (4):