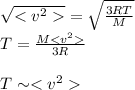Answer:
the square of the average atomic velocity.
Step-by-step explanation:
From the formulas for kinetic energy and temperature for a monoatomic gas, which has three translational degrees of freedom, the relationship between root mean square velocity and temperature is as follows:
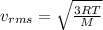 (1)
(1)
Where
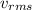 is the root mean square velocity, M is the molar mass of the gas, R is the universal constant of the ideal gases and T is the temperature.
is the root mean square velocity, M is the molar mass of the gas, R is the universal constant of the ideal gases and T is the temperature.
The root mean square velocity is a measure of the velocity of the particles in a gas. It is defined as the square root of the mean square velocity of the gas molecules:
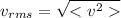 (2)
(2)
substituting 2 in 1, we find the relationship between mean square speed and temperature: