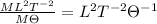Answer:
Dimension of specific heat will be
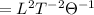
Step-by-step explanation:
We know that heat
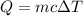 , Q is heat generated, m is mass, c is specific heat and
, Q is heat generated, m is mass, c is specific heat and
 is temperature difference
is temperature difference
From formula we can write
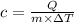
Now unit of Q is joule or N-m
Newton can be written as
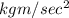
So unit of Q is
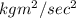
For dimension we use M for kg, L for meter(m) ,T for sec and
 for temperature
for temperature
So dimension of Q is
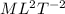
So dimension of specific heat will be