Answer:
The density of carbon dioxide is 1,86 g/L
Step-by-step explanation:
The global reaction is:
2 HCl (aq)+ CaCO₃ (s) → CaCl₂(aq)+ H₂O(l)+ CO₂(g)
To obtain density it is necessary to obtain calcium carbonate moles -with molar mass of CaCo₃ = 100,09 g/mol- that are the same than CO₂ moles. Then, this moles must be converted to grams -CO₂ weights 44,01 g/mol- and, with the given liters (225 L) will be possible to know density, thus:
1004,0g × 95,0% = 953,8 g of CaCO₃
953,8 g of CaCO₃ ×
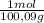 =
=
9,53 CaCO₃ moles ≡ CO₂ moles
9,53 CO₂ moles ×
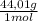 = 419,4 g of CO₂
= 419,4 g of CO₂
Thus, density of Carbon dioxide is:
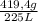 = 1,86 g/L
= 1,86 g/L
I hope it helps!