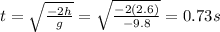Answer:
0.73 s
Step-by-step explanation:
The glass is in free fall, so its vertical position at time t is given by the equation:
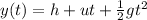
where
h = 2.6 m is the initial height
u = 0 is the initial velocity of the glass
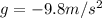 is the acceleration of gravity (downward since it is negative)
is the acceleration of gravity (downward since it is negative)
We want to know the time t at which the glass reaches the ground, so when
y(t) = 0
So the equation becomes
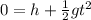
And solving for t, we find