Answer:
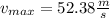
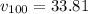
Step-by-step explanation:
the maximum speed is reached when the drag force and the weight are at equilibrium, therefore:
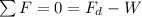
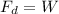
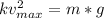
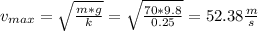
To calculate the velocity after 100 meters, we can no longer assume equilibrium, therefore:
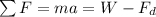
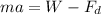
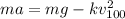
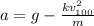 (1)
(1)
consider the next equation of motion:
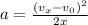
If assuming initial velocity=0:
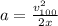 (2)
(2)
joining (1) and (2):
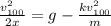
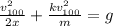
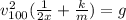
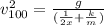
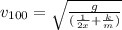 (3)
(3)
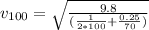
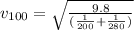
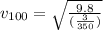
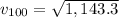
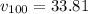
To plot velocity as a function of distance, just plot equation (3).
To plot velocity as a function of time, you have to consider the next equation of motion:
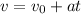
as stated before, the initial velocity is 0:
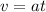 (4)
(4)
joining (1) and (4) and reducing you will get:
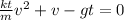
solving for v:
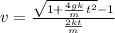
Plots: