Answer : The correct option is, (B) 0.25 atm
Explanation :
Combined gas law is the combination of Boyle's law, Charles's law and Gay-Lussac's law.
The combined gas equation is,
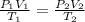
where,
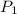 = initial pressure of gas = 0.99 atm
= initial pressure of gas = 0.99 atm
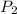 = final pressure of gas = ?
= final pressure of gas = ?
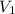 = initial volume of gas = 2.00 L
= initial volume of gas = 2.00 L
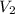 = final volume of gas =
= final volume of gas =
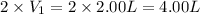
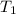 = initial temperature of gas = 273 K
= initial temperature of gas = 273 K
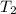 = final temperature of gas = 137 K
= final temperature of gas = 137 K
Now put all the given values in the above equation, we get:
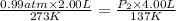
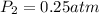
Therefore, the final pressure of the gas is 0.25 atm.