Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
given data:
innner radius r_i = = 5cm
outer radius r_0 = 7 cm
temperature at outer surface = 80 degree celcius
temperature at inner surface = 100 degree celcius
thermal resistance per unit length is given as
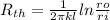
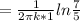
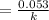
heat loss rate per unit length
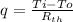
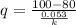
q = 373.474 K
1) for pure COPPER
k = 387 W/m degree celcius
q = 373.474 * 387 = 144534.438 W
2) for pure ALUMINIUM
k = 200 W/m degree celcius
q = 373.474 * 200 = 74694.84 W
3)
1) for pure IRON
k = 62W/m degree celcius
q = 373.474 * 62 = 23155.416 W