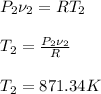Answer:
T2=871.34 K = 598.19 °C
Step-by-step explanation:
As the relation Pv^k=cte is not clear, I will assume that k=3
Now, the first step is to find the specific molar volume in state 1, we use ideal gas law to find it:
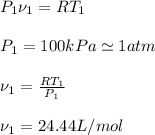
Now, to find the value of v2, we use the polytropic relation:
![P_(1) \\u _(1) ^(3)=P_(2) \\u _(2) ^(3)\\\\\\u _(2) ^(3)=(P_(1) \\u _(1) ^(3))/(P_(2)) \\\\\\u _(2)=\sqrt[3]{(P_(1) \\u _(1) ^(3))/(P_(2))} \\\\\\u_(2)=14.29L/mol](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/ra5acs58hfgzblxa9350duj645laocv1ve.png)
With the value of v2, we can calculate the temperature in the second state with ideal gas law: