Step-by-step explanation:
According to the first law of thermodynamics,
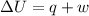
When there is no work done then, w = 0.
As, 0.5 mole of sugar generates heat (q) = -2000 kJ
So, amount of heat (q) generated by 1 mole of sugar will be calculated as follows.
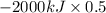
= -1000 kJ
So, putting the values into the above formula as follows.
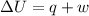
= -1000 kJ + 0
= -1000 kJ
Also, according to the definition of enthalpy the relation between enthalpy and internal energy is as follows.
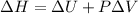
As change in volume is 0.
Hence,
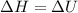
= -1000 kJ
Thus, we can conclude that the change in enthalpy of the system(
 ) is -1000 kJ.
) is -1000 kJ.