Answer:
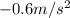 (to the left)
(to the left)
Step-by-step explanation:
The question is missing in the text. The complete text of the problem is:
"A skateboarder is moving to the right with a velocity of 8 m/s. After a steady gust of wind that lasts 5 s, the skateboarder is moving to the right with a velocity of 5 m/s. Assuming the acceleration is constant, what is the acceleration of the skateboarder during the 5 s time period?"
Solution:
The acceleration of the skateboarder is given by:
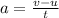
where
a is the acceleration
v is the final velocity after a time t
u is the initial velocity
t is the time interval
In this problem, taking the right as positive direction, we have:
u = +8 m/s (to the right)
v = +5 m/s (to the right)
t = 5 s
Substituting into the equation, we find
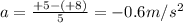
And the negative sign means the acceleration is towards the left.