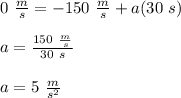Answer: OPTION D.
Step-by-step explanation:
We can use the Kinematic formula for an object under constant acceleration:
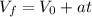
Where
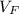 is the final velocity,
is the final velocity,
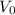 is the initial velocity, "a" is the acceleration and "t" is the time.
is the initial velocity, "a" is the acceleration and "t" is the time.
In this case we know that:
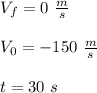
Therefore, we must substitute these values into the formula and solve for "a":