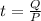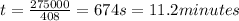Answer:
R = 35.3 ohms
It would take 11.2 minutes
Step-by-step explanation:
Ohm's law states that
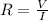
Therefore:
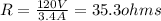
Joule's law states that
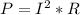
So
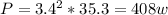
I assume the problem means 780 g of ice.
The specific heat capacity of ice is:
Cp = 2 kJ/(kg*K)
And the latent heat to melt ice is:
Cl = 333 kJ/kg
So, the heat needed to melt ice from -10 C is:
Q = m * Cp * (tfinal - ti) + m * Cl
Q = 0.78 * (2 * (0 - (-10)) + 333) = 275 kJ
Power is energy over time
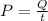
so with a power of P it would take t seconds to deliver an energy Q