Answer : E) none of these.
The vapor pressure of solution is 637 torr .
Solution :
As the relative lowering of vapor pressure is directly proportional to the amount of dissolved solute.
The formula for relative lowering of vapor pressure will be,
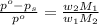
where,
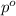 = vapor pressure of pure solvent (water) = 760 torr
= vapor pressure of pure solvent (water) = 760 torr
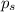 = vapor pressure of solution = ?
= vapor pressure of solution = ?
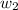 = mass of solute (ethylene glycol) = 557.1 g
= mass of solute (ethylene glycol) = 557.1 g
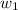 = mass of solvent (water) = 1000.0 g
= mass of solvent (water) = 1000.0 g
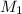 = molar mass of solvent (water) = 18.02 g/mole
= molar mass of solvent (water) = 18.02 g/mole
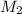 = molar mass of solute (ethylene glycol) = 62.07 g/mole
= molar mass of solute (ethylene glycol) = 62.07 g/mole
Now put all the given values in this formula ,we get the vapor pressure of the solution.
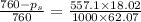
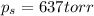
Therefore, the vapor pressure of solution is, 637 torr.