Answer: Option (b) is the correct answer.
Step-by-step explanation:
A buffer is defined as a solution which does not lead to any change in pH of a solution upon addition of an acid or base.
For example,
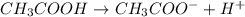
Here,
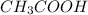 is the acid and
is the acid and
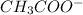 is its conjugate base.
is its conjugate base.
So, when we add a conjugate base into an acid then it helps in neutralization of the solution.
Thus, we can conclude that a buffer can neutralize acid because the conjugate base grabs
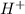 ion.
ion.