Answer:
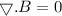 is proved.
is proved.
Step-by-step explanation:
The magnetic field in the long current carrying wire is,
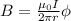
Here, I is the current, B is the magnetic field.
Now, by using cylindrical coordinates for the divergence of B.
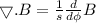
Put the value of B in above equation.
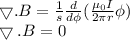
Hence, it is prove that for a long current I carrying wire magnetic field divergence that is
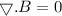 .
.