Answer:
The answer is 11.7 ft
Step-by-step explanation:
You can use the combined gas law from Boyle's law, Charles's law, and Gay-Lussac's Law. Only because hydrogen behaves like an ideal gas for this conditions.

where the subscripts denote the pressure "p", volume "V" and the temperature "T" (in Kelvin) at two different times. Let's consider
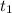 as the balloom at 150,000 ft so
as the balloom at 150,000 ft so
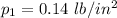
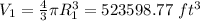
and
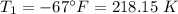 .
.
Then,
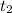 is the moment when the balloon is on the ground.
is the moment when the balloon is on the ground.
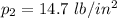 and
and
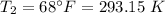 .
.
From the first equation,
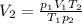 , then
, then
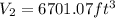 and the radius would be
and the radius would be
![R_2 = \sqrt[3]{(3 V_2)/(4 \pi)} = 11.7 \ ft](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/9ob9qkwo575o2j3jw5ec7xgpljv53tnkhy.png) .
.