Based on the given parameters, the magnitude of the acceleration is approximately 49.376 m/
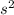 .
.
How to find the magnitude of the acceleration
To find the magnitude of the acceleration, use the equation below;
|a| = |Δv| / Δt
where |Δv| is the magnitude of the change in velocity and Δt is the time interval.
Given:
Initial velocity (vi) = 2.35 m/s at -22.0°
Final velocity (vf) = 6.42 m/s at 50.0°
Time interval (Δt) = 0.125 s
To calculate the change in velocity, subtract the initial velocity vector from the final velocity vector:
Δv = vf - vi
To perform vector subtraction, break down the velocities into their horizontal (x) and vertical (y) components:
Initial velocity components:
vix = vi * cos(-22.0°)
viy = vi * sin(-22.0°)
Final velocity components:
vfx = vf * cos(50.0°)
vfy = vf * sin(50.0°)
Now calculate the change in velocity components:
Δvx = vfx - vix
Δvy = vfy - viy
The magnitude of the change in velocity is given by the Pythagorean theorem:
|Δv| =
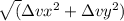
Finally, calculate the magnitude of the acceleration:
|a| = |Δv| / Δt
Let's compute these values:
vix = 2.35 m/s * cos(-22.0°) ≈ 2.086 m/s
viy = 2.35 m/s * sin(-22.0°) ≈ -0.856 m/s
vfx = 6.42 m/s * cos(50.0°) ≈ 4.100 m/s
vfy = 6.42 m/s * sin(50.0°) ≈ 4.905 m/s
Δvx = 4.100 m/s - 2.086 m/s ≈ 2.014 m/s
Δvy = 4.905 m/s - (-0.856 m/s) ≈ 5.761 m/s
|Δv| =
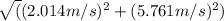 ≈ 6.172 m/s
≈ 6.172 m/s
|a| = 6.172 m/s / 0.125 s ≈ 49.376 m/
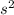
Therefore, the magnitude of the acceleration is approximately 49.376 m/
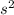 .
.