Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
From the combustion of carbon, the reactions occurring in limited oxygen conditions are:
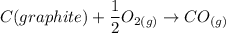
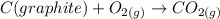
If it occurs in excess, then any leftover CO changes to CO2. i.e.
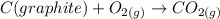 ---- (1)
---- (1)
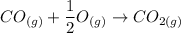 ----- (2)
----- (2)
From (1), the enthalpy change is:
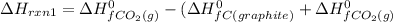
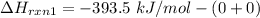
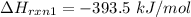
From (2), the enthalpy change is:
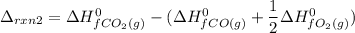
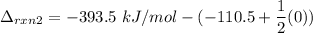
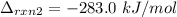
Subtracting (2) from (1), we get:
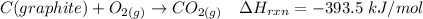
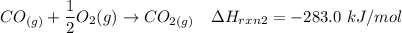
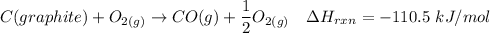
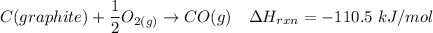
The enthalpy change ΔH of the reaction = -110.5 kJ/mol