Step-by-step explanation:
We assumes that all the electrical energy produced will be converted into the heat energy.
Electrical energy input = Heat energy absorbed by object = Heat energy required = Q
As, Q = U - W
= U - RT
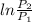
Since, it is given that U = 286.1 kJ/kg,
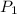 is 600 kPa,
is 600 kPa,
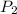 is 200 kPa, and T is 400 K.
is 200 kPa, and T is 400 K.
Therefore, putting these given values into the above formula is as follows.
Q = U - RT
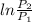
=
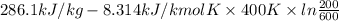
=
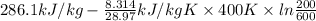
= 412.27 kJ/kg
Thus, we can conclude that the electrical energy supplied to air is 412.27 kJ/kg.